P(x y) joint probability 117803-What does p(x y) mean
1 A perfectly symmetric die that is equally likely to land on any of its 6 sides is thrown twice Let X be the upturned value of the first throw, and let Y be the sum of the two upturned values Find the joint probability mass function of X and Y 2 Seventy percent of the graduate students at the local university are domestic and thirty percent are internationalThe joint probability formula If the probability of rolling a six on one die is P (X) and the probability of rolling a six on the second die P (Y), we can use the formula P (X,Y) = P (X) * P (Y)Question Back To Top (10 Points) Problem 3 The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X And Y P(x,y), Is Given By 1 1 1 P(2,1) 9' P(3,1) 1 1 P(1,2) 9 P(2,2)=0, P(3,2) 18 1 P(1,3)=0, P(2,3) P(3,3) 9 Part A Compute EXY = Iſ For Each Of I=1,2,3 You May Perform The Actual Calculation In Python, But You Must Show By Hand (in Markdown/MathJax/by Actual Hand) Your
Pradeepchandrasekar Weebly Com Uploads 4 7 8 2 Unit 2 03 Pdf
What does p(x y) mean
What does p(x y) mean-Figure1 f(x;y)j0 < x < 1;0 < y < 1g Note that f(x;y) is a valid pdf because P (1 < X < 1;1 < Y < 1) = P (0 < X < 1;0 < Y < 1) = Z1 1 Z1 1 f(x;y)dxdy = 6 Z1 0 Z1 0 x2ydxdy = 6 Z1 0 y 8 < Z1 0 x2dx 9 =;If X is a random variable with density fx(x) and Y is a random variable with density fY(y), how would we describe the joint behavior of the tuple (X, Y) at the same time?The



Show That The Following Function Satisfies The Properties Of A Joint Probability Mass Function Determine The Following A P X 2 5 Study Com
Joint probability p(A and B) The probability of event A and event B occurring It is the probability of the intersection of two or more events The probability of the intersection of A and B may be written p(A ∩ B) Example the probability that a card is a four and red =p(four and red) = 2/52=1/26Therefore, the joint probability of event "A" and "B" is P(4/52) x P(26/52) = = 39% More Resources CFI is the official provider of the global Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ FMVA® Certification Join 350,600 students who work for companies like Amazon, JP Morgan, and Ferrari certification program, designedP(A,B) = 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/36 Joint Probability Table A joint probability distribution represents a probability distribution for two or more random variables Instead of events being labelled A and B, the condition is to use X and Y as given below f(x,y) = P(X = x, Y = y) The main purpose of this is to look for a relationship between two
Dy = 6 Z1 0 y 3 dy = 1 Following the de–nition of the marginal distribution, we can get a marginal distribution for X For 0 < x < 1, f(x) ZP(X = x i, Y = y j) = P(X = x i) ∩ (Y = y j) = p ij 2 It should satisfies the following conditions (i) p ij ≥ ∀ i, j (ii) Σ j Σ i p ij = 1 12 Marginal Probability Function of X If the joint probability distribution of two random variables X and Y is given then the marginal probability function of X is given byP(X=A) = sum P(X=A, Y=yi) for all y This is another important foundational rule in probability, referred to as the " sum rule " The marginal probability is different from the conditional probability (described next) because it considers the union of all events for the second variable rather than the probability of a single event
But avoid Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers(Joint probability function) If X and Y are discrete random variables, n the function f(x i, y i)=P(X=x i, Y=y i)=P ij is called the joint probability function for the discrete random variables X and Y if and only if f(x i, y i) satisfies the following conditions 1 f(x i, y i)=P ij ≥0, for all i, j 2 ∑ i ∑ i p i j = 1Thanks for contributing an answer to Mathematics Stack Exchange!



Statistical Sciences 2141a B Lecture Notes Fall 18 Lecture 14 Probability Density Function Probability Mass Function Joint Probability Distribution



Transformations Of A Continuous Random Variable
Math 370/408, Actuarial Problemsolving AJ Hildebrand 5 Independence of random variables • Definition X and Y are called independent if the joint pmf is the product of theJoint probability is a statistical measure that calculates the likelihood of two events occurring together and at the same point in time Joint probability is the probability of event Y occurring• Discrete Random vector The joint distribution of (X,Y) can be described by the joint probability function {pij} such that pij = P(X = xi,Y = yj) We should have pij ≥ 0 and X i X j pij = 1



Solved Let The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X And Y Chegg Com


Solved Suppose Random Variables X And Y Have Joint Probability Density Function F X Y 63 Quot 3 23 For 0 Lt X Lt Y Lt 00 0 Otherwise Course Hero
• Jointprobabilitymassfunction PX,Y (x,y)=P(X = x,Y =y) • The probability of event {(X,Y)∈ B} is P(B)= X (x,y)∈B PX,Y (x,y) – Two coins, one fair, the other twoheaded A randomly chooses one and B takes the other X = ˆ 1 A gets head 0 A gets tail Y = ˆ 1 B gets head 0 B gets tail Find P(X ≥ Y) • Marginal probability mass function of X can be obQuestion The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Y Is Given As Follows Find P(X =Y) P(x,y) Y 1 15/66 12/66 2 3/66 0 10/66 /66 6/66 0 1 2 A B 2/3 5/33 2/11 1/3 C D This question hasn't been answered yet Ask an expertStack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange
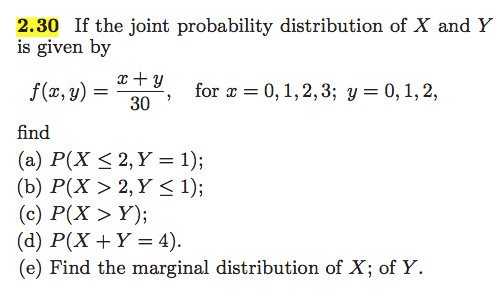


Solved If The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Y I Chegg Com


Ppt Probability Theory Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Suppose the joint pmf of X and Y isgiven byp(1,1) = 05, p(1,2) = 01, p(2,1) = 01, p(2,2) = 03 Find the pmf of X given Y = 1 sults in a success with probability p Compute the expected number of successes in the first n trials given that there are k successes in all Solution Let Y be the number of successes in nmPlease be sure to answer the questionProvide details and share your research!Joint probability cannot be used to determine how much the occurrence of one event influences the occurrence of another event Therefore the joint probability of X and Y (two dependent events) will


Http Www Stat Osu Edu Mb Chap5 427 Pdf



St 371 Viii Theory Of Joint Distributions Pdf Free Download
Y 1,2,3 Find all the marginal and conditional probability distributions Also find the probability distribution of X YIn the discrete case, recall that every ordered pair of outcomes (x, y) (x,y) (x, y) is assigned the probability p (x, y) p (x,y) p (x, y) Since the discrete case is discrete, these may be thought of as matrix elements p i j p_{ij} p i j by ordering the possible outcomes in some way, where each fixed i i i corresponds to fixed x x x and viceIf the points in the joint probability distribution of X and Y that receive positive probability tend to fall along a line of positive (or negative) slope, ρ XY is near 1 (or −1) If ρ XY equals 1 or −1, it can be shown that the points in the joint probability distribution that receive positive probability fall exactly along a straight line Two random variables with nonzero correlation are said to be correlated


Http Homepage Stat Uiowa Edu Rdecook Stat Hw Hw7 Pdf


Faculty Math Illinois Edu Hildebr 370 370jointdistributions Pdf
JOINT PROBABILITY – It is the possibility of occurring one or more independent events at the same time For instance, if an event Y appears and the same time event X appears, it is called a joint probabilityGiven a pair of discrete random variables X, Y, which takes values from alphabets J X, J Y and have probability mass functions p X = {p(x)} and p Y = {p(y)}, respectively 1 H(X) ≥ 0, with equality if and only if X is deterministic 2 H(XY) ≥ 0, or equivalently H(X, Y) ≥ H(Y) 3Given information The joint probability mass function of X and Y is given X can take values 1 and 2 and Y also takes values 1 and 2 (a) The required probability will be given as,


Http Math Unm Edu Knrumsey Classes Fall17 Homeworks Chapter5 Pdf


Conf Math Illinois Edu Rsong 461f10 Lect6 Pdf
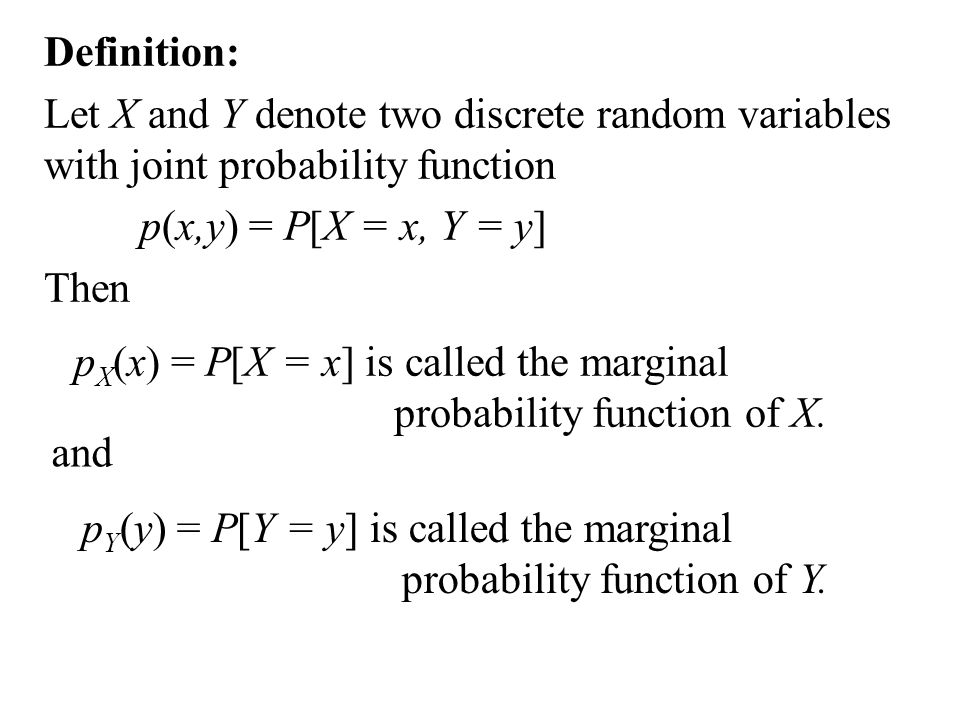
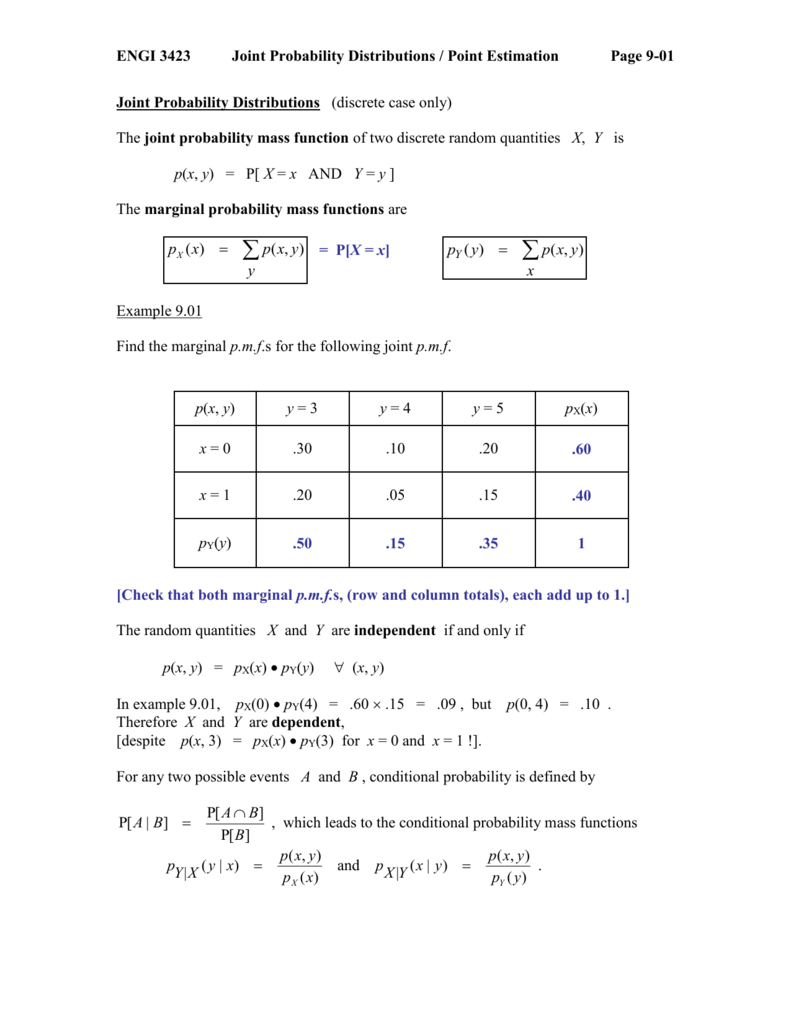
Marginal Probability Mass Function If X and Y are discrete random variables with joint probability mass function fXY(x;y), then the marginal probability mass functions of Xand Y are fX(x) = X y fXY(x;y) and fY(y) = X x fXY(x;y) where the sum for fX(x) is over all points in the range of (X;Y) for which X= xand the sum for fY(y) is over all points in the rangeExample 5 X and Y are jointly continuous with joint pdf f(x,y) = (e−(xy) if 0 ≤ x, 0 ≤ y 0, otherwise Let Z = X/Y Find the pdf of Z The first thing we do is draw a picture of the support set (which in this case is the first1 A perfectly symmetric die that is equally likely to land on any of its 6 sides is thrown twice Let X be the upturned value of the first throw, and let Y be the sum of the two upturned values Find the joint probability mass function of X and Y 2 Seventy percent of the graduate students at the local university are domestic and thirty percent are international



Joint Probability Distributions And Random Samples Whelan Courses 10 4wi 1016 345 Probability Distributions Pdf Document



Introduction To Marginal And Conditional Probability Using Python Numpy Examples And Drawings
Dy = 6 Z1 0 y 3 dy = 1 Following the de–nition of the marginal distribution, we can get a marginal distribution for X For 0 < x < 1, f(x) ZIf the points in the joint probability distribution of X and Y that receive positive probability tend to fall along a line of positive (or negative) slope, ρ XY is near 1 (or −1) If ρ XY equals 1 or −1, it can be shown that the points in the joint probability distribution that receive positive probability fall exactly along a straightIn other words, it is the amount by which the uncertainty of one random variable is reduced due to the knowledge of another It is defined as the relative entropy between the joint distribution p(x, y) and the product distribution p(x)p(y) of two random variables X and Y (Subsititute p(x, y) for p(x), and p(x)p(y) for q(x) in (26))


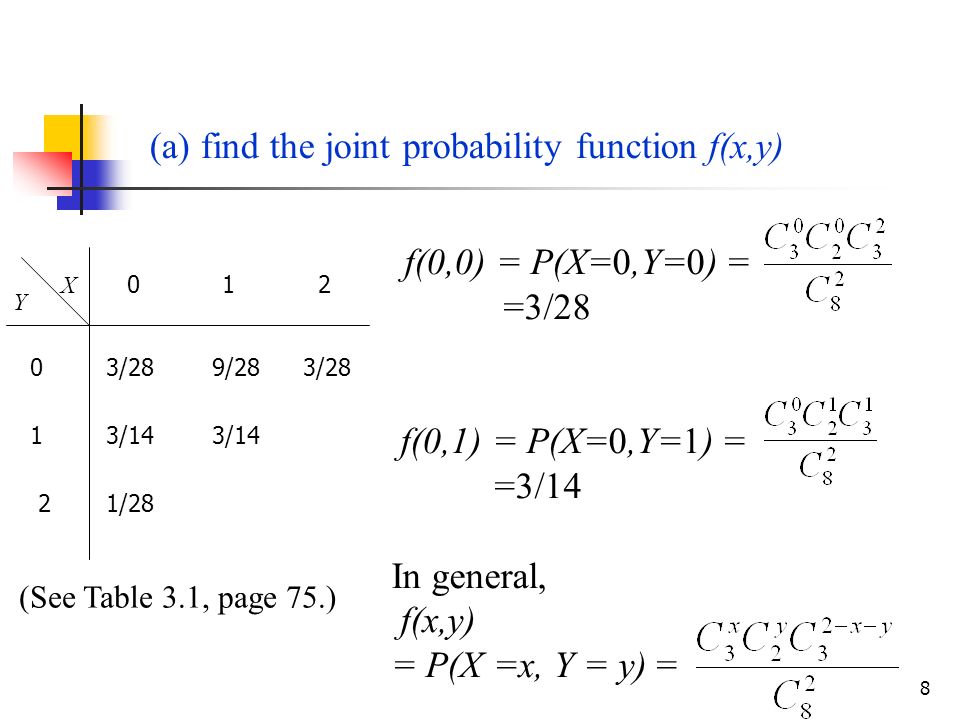
2
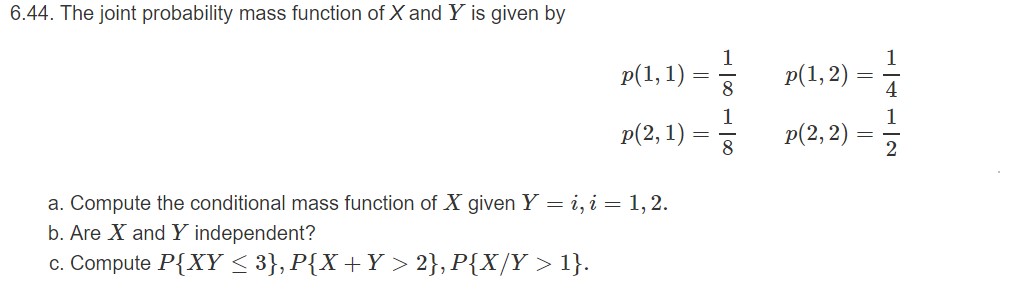


Answered 6 44 The Joint Probability Mass Bartleby
The joint probability mass function of X Y, is given p(x, y) k (2x 3y), x 0,1,2;If discrete random variables X and Y are defined on the same sample space S, then their joint probability mass function (joint pmf) is given by p (x, y) = P (X = x and Y = y), where (x, y) is a pair of possible values for the pair of random variables (X, Y), and p (x, y) satisfies the following conditions 0 ≤ p (x, y) ≤ 1Joint probability distribution p(X;Y) models probability of cooccurrence of two rv X, Y For discrete rv, the joint PMF p(X;Y) is like a table (that sums to 1) X x X y p(X = x;Y = y) = 1 For continuous rv, we have joint PDF p(X;Y) Z x Z y p(X = x;Y = y)dxdy = 1 (IITK) Basics of Probability and Probability Distributions 7



Conditional Probability Of Joint Discrete Random Variables Mathematics Stack Exchange


Pradeepchandrasekar Weebly Com Uploads 4 7 8 2 Unit 2 03 Pdf
F (x, y) = ax^2 by is a joint probability distribution function of X, Y and 0 less than x less than 1, 0 less than y less than 2 Given that a b = 2, Find P(x less than 05)P(X, Y) 2A = Z A Z f(x, y)dxdy fis now called thejoint probability density functionand must satisfy 1 f(x, y) 0 for 1The joint probability mass function of (X;Y) is (12) p(xi;yj) = P(X = xi;Y = yj) Example 1 A fair coin is tossed three times independently let X denote the number of heads on the flrst toss and Y denote the total number of heads Find the joint probability mass function of X and Y 2



Q3 Suppose That Joint Probability Function Of X And Y Is Given By 1 7 Homeworklib



1 Point 1 Old Quiz Question Let X And Y Have The Joint Probability Density Function Homeworklib
Heads obtained by B Find P(X > Y) • Discrete case Joint probability mass function p(x,y) = P(X = x,Y = y) – Two coins, one fair, the other twoheaded A randomly chooses one and B takes the other X = ˆ 1 A gets head 0 A gets tail Y = ˆ 1 B gets head 0 B gets tail Find P(X ≥ Y) 1Figure1 f(x;y)j0 < x < 1;0 < y < 1g Note that f(x;y) is a valid pdf because P (1 < X < 1;1 < Y < 1) = P (0 < X < 1;0 < Y < 1) = Z1 1 Z1 1 f(x;y)dxdy = 6 Z1 0 Z1 0 x2ydxdy = 6 Z1 0 y 8 < Z1 0 x2dx 9 =;For continuous variables, we define the joint probability density function p(x,y) on (some subset of) the plane of pairs of real numbers We interpret the function as follows p(x,y)dxdy is (approximately) the probability that X is between x and xdx and Y is between y and ydy (with error that goes to zero faster than dx and dy as they both go to zero)


Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download



The Random Variable X And Y Have The Following Joint Probability Mass Function P X Y 23 0 2 Homeworklib
• Jointprobabilitymassfunction PX,Y (x,y)=P(X = x,Y =y) • The probability of event {(X,Y)∈ B} is P(B)= X (x,y)∈B PX,Y (x,y) – Two coins, one fair, the other twoheaded A randomly chooses one and B takes the other X = ˆ 1 A gets head 0 A gets tail Y = ˆ 1 B gets head 0 B gets tail Find P(X ≥ Y) • Marginal probability massFor continuous random variables, we have the notion of the joint (probability) density function f X,Y (x,y)∆x∆y ≈ P{x < X ≤ x∆x,y < Y ≤ y ∆y} We can write this in integral form as P{(X,Y) ∈ A} = Z Z A f X,Y (x,y)dydx The basic properties of the joint density function are • f X,Y (x,y) ≥ 0 for all x and y 2If X is a random variable with density fx(x) and Y is a random variable with density fY(y), how would we describe the joint behavior of the tuple (X, Y) at the same time?The


The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X And Y Is Given By Px Y 1 1 Px Y 1 2 3 Px Y 1 3 00 1 Px Y 2 1 Px Y 2 2 3 Course Hero


Http Home Ku Edu Tr Mmuradoglu Engr1 Engr1hw5sol Pdf
Difference Between Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Probability JOINT PROBABILITY – It is the possibility of occurring one or more independent events at the same time For instance, if an event Y appears and the same time event X appears, it is called a joint probabilityFor continuous random variables, we have the notion of the joint (probability) density function f X,Y (x,y)∆x∆y ≈ P{x < X ≤ x∆x,y < Y ≤ y ∆y} We can write this in integral form as P{(X,Y) ∈ A} = Z Z A f X,Y (x,y)dydx The basic properties of the joint density function are • f X,Y (x,y) ≥ 0 for all x and y 2Question The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Y Is Given As Follows Find P(X =Y) P(x,y) Y 1 15/66 12/66 2 3/66 0 10/66 /66 6/66 0 1 2 A B 2/3 5/33 2/11 1/3 C D This question hasn't been answered yet Ask an expert



Joint Probability Distribution Wikipedia


Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download
This is not really any different from what we've already seenP(A,B) = 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/36 Joint Probability Table A joint probability distribution represents a probability distribution for two or more random variables Instead of events being labelled A and B, the condition is to use X and Y as given below f(x,y) = P(X = x, Y = y) The main purpose of this is to look for a relationship between twoSolution for Example Suppose that p(x, y), the joint probability mass function of X and Y, is given by p(0,0) = 025 p(0,1) 1Calculate the conditional
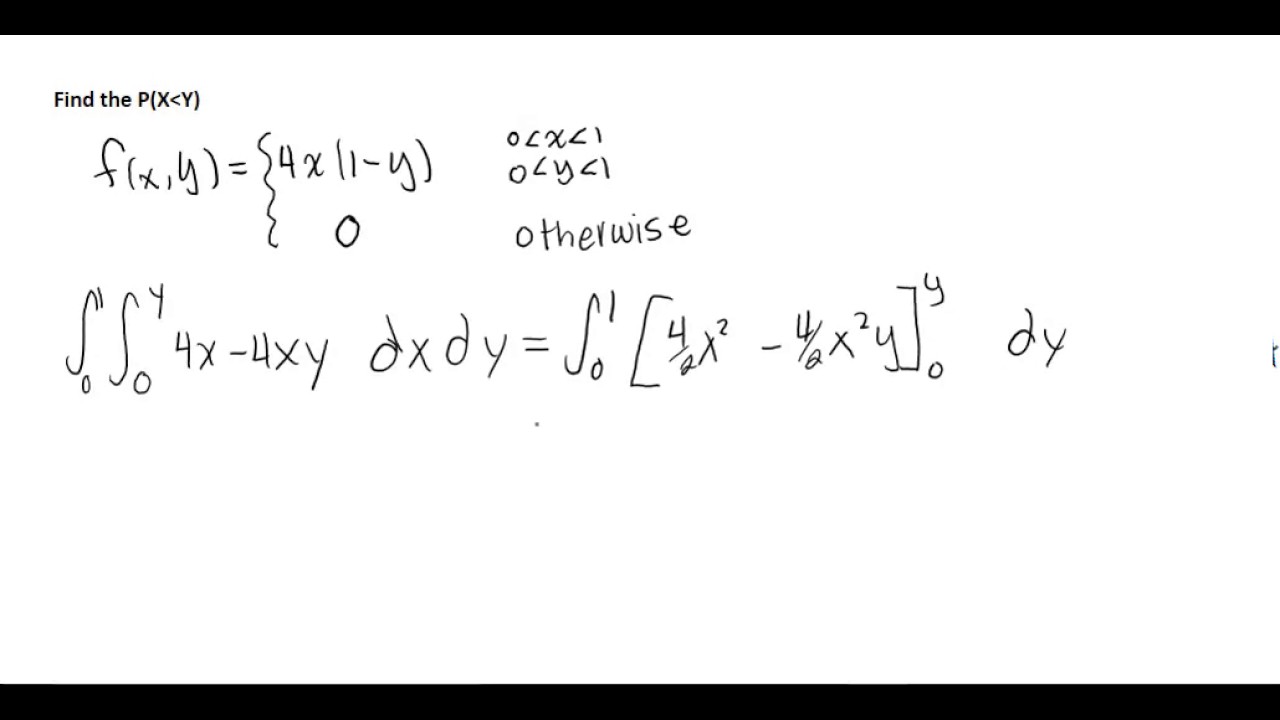


P X Less Than Y From Joint Pdf Youtube



Chapter 5 Joint Probability Distributions Part 1 Sections 5
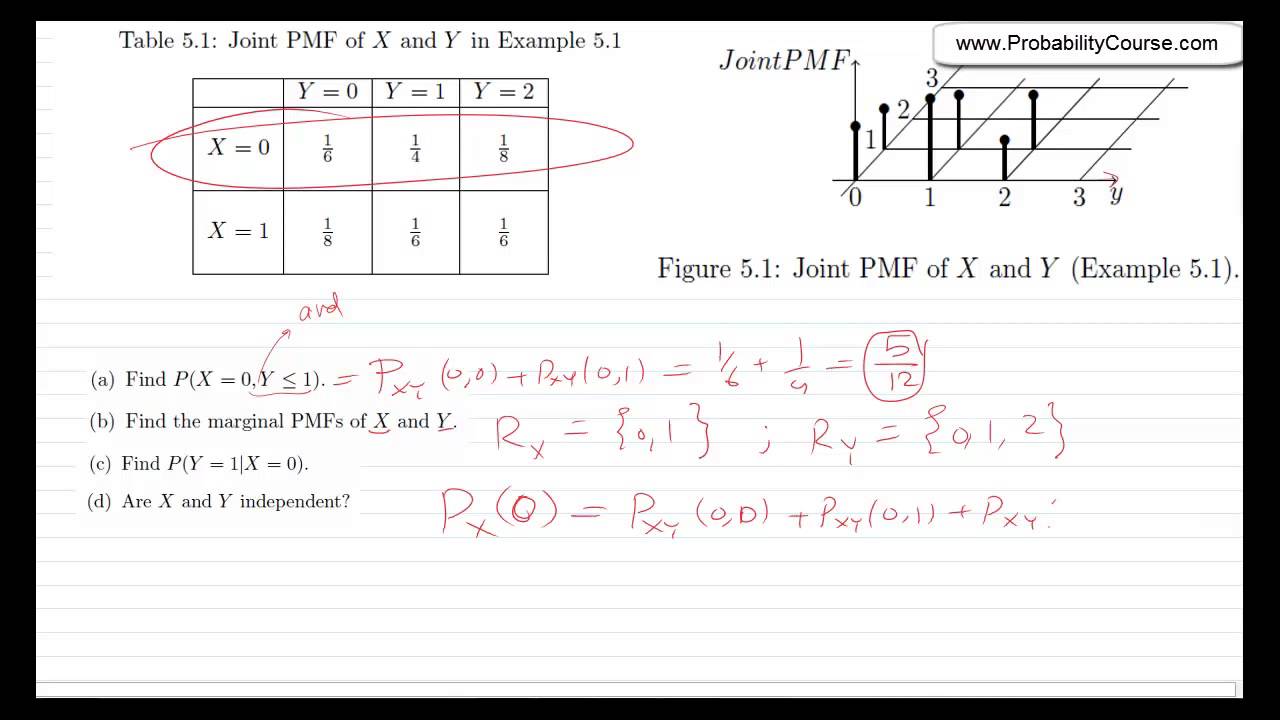
The sum of all probabilities still add to 1, since this, too, is a probability distribution We could define the first coin's outcome as the X X and the second as Y Y and write P (X = H,Y = H) = 025 P (X = H, Y = H) = 025 Don't be fooled, though!


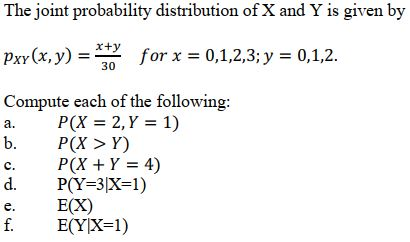
2



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides



13cond Joint Probability Distributions Example Let X And Y Be Jointly Continuous Random Variables Having Joint Density F X Y For 0 X Y 1 Otherwise Course Hero



How To Find The Mean And Variance Of Minimum Of Two Dependent Random Variables


Http Homepage Stat Uiowa Edu Rdecook Stat Notes Ch5 Pt1 Pdf



Joint Probability Distribution Wikipedia


Joint Probability Distributions


Http Www Cl Cam Ac Uk Teaching 1314 Infotheory Exercises1to4 Pdf


38 Joint Probability Mass Function Pmf Youtube


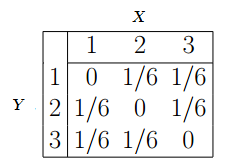
2


Q Tbn And9gct1ck8fpzmvcy09br Jwxhbrf6s Byf2nrqxvsl2thghbrtwelt Usqp Cau


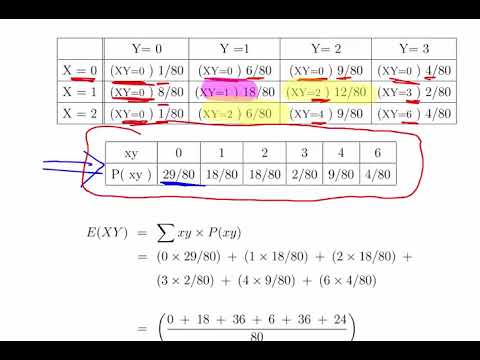
2



Product Distribution Wikipedia


Http Home Ku Edu Tr Mmuradoglu Engr1 Engr1hw5sol Pdf
/JointProbabilityDefinition2-fb8b207be3164845b0d8706fe9c73b01.png)


Joint Probability Definition


Http Math Arizona Edu Jwatkins Joint Pdf


Http Www2 Siit Tu Ac Th Prapun Ecs315 18 1 Ecs315 Hw 18 12 Sol u1 Pdf


Causal Representation Of Signal Response Models The Joint Probability Download Scientific Diagram


3 4 Joint Probability Distributions Ppt Video Online Download


Solved The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Y Is G Chegg Com



Show That The Following Function Satisfies The Properties Of A Joint Probability Mass Function Determine The Following A P X 2 5 Study Com


Joint Probability And Joint Distributions Definition Examples Statistics How To


Nptel Ac In Content Storage2 Courses Assignments Test Set 6 Pdf



Problems And Solutions 4



Poison Distribution Homework Help


Joint Probability Distributions Of Discrete Random Variables Youtube


Joint Probability Density Function Joint Continuity Pdf



Chapter 4 Joint And Conditional Distributions Ppt Download


Www Stt Msu Edu Users Makagon 351 5 1 Pdf


Http Homepage Divms Uiowa Edu Rdecook Stat Notes Ch5 Pt2 Pdf


Faculty Math Illinois Edu Hildebr 370 Problemsets Problemset4s Pdf
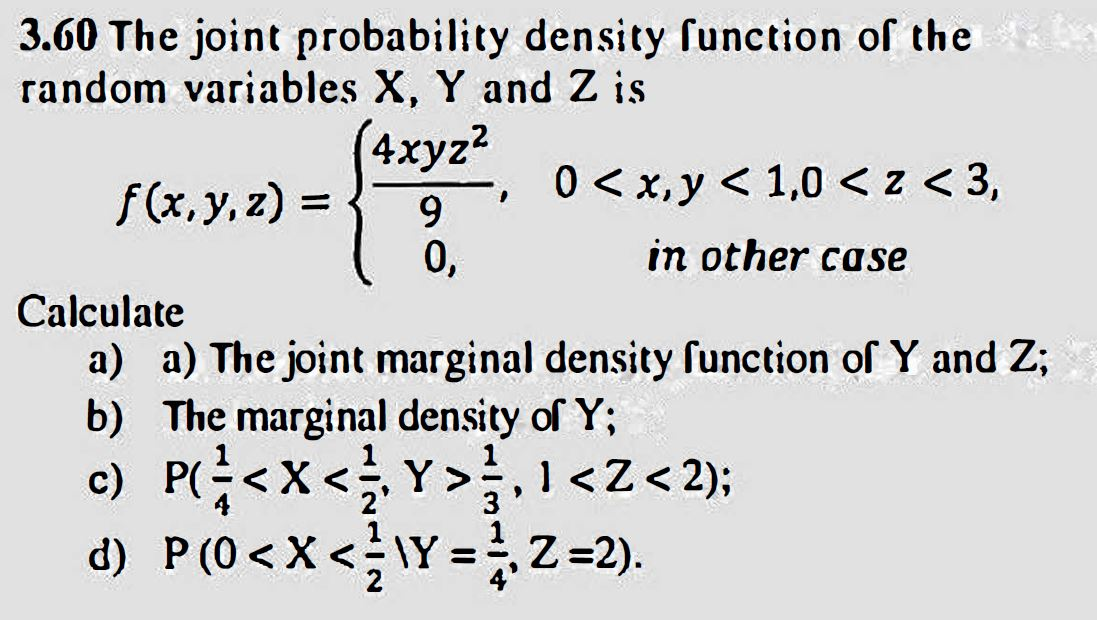


Solved 3 60 The Joint Probability Density Function Of The Chegg Com



2 The Joint Probability Density Function Of X And Chegg Com


Lesson 17 Distributions Of Two Discrete Random Variables


Lesson 17 Distributions Of Two Discrete Random Variables



Joint Probability Distribution In Quantitative Techniques For Management Tutorial 11 March 21 Learn Joint Probability Distribution In Quantitative Techniques For Management Tutorial Wisdom Jobs India


Joint Probability Distribution


2


Http Faculty Atu Edu Mfinan 3153 Section26 Pdf
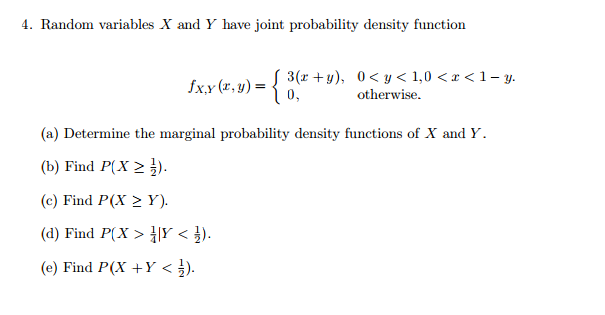


Solved 4 Random Variables X And Y Have Joint Probability Chegg Com


Joint Probability Distributions



Question Answer Joint Distributions And Independent Variables 2 54 The Joint Probability Function Of Two Discrete Random Variables Grand Paper Writers



Find P X Y Le 0 Given The Joint Probability Function Of X And Y Mathematics Stack Exchange



Answered Section 2 6 Given The Joint Bartleby


Www Math Uh Edu Bekki 3339 Notes 3339day11done Pdf



St 371 Viii Theory Of Joint Distributions Pdf Free Download


Search Q Bayes Theorem Tbm Isch


Joint Probability Distributions



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides
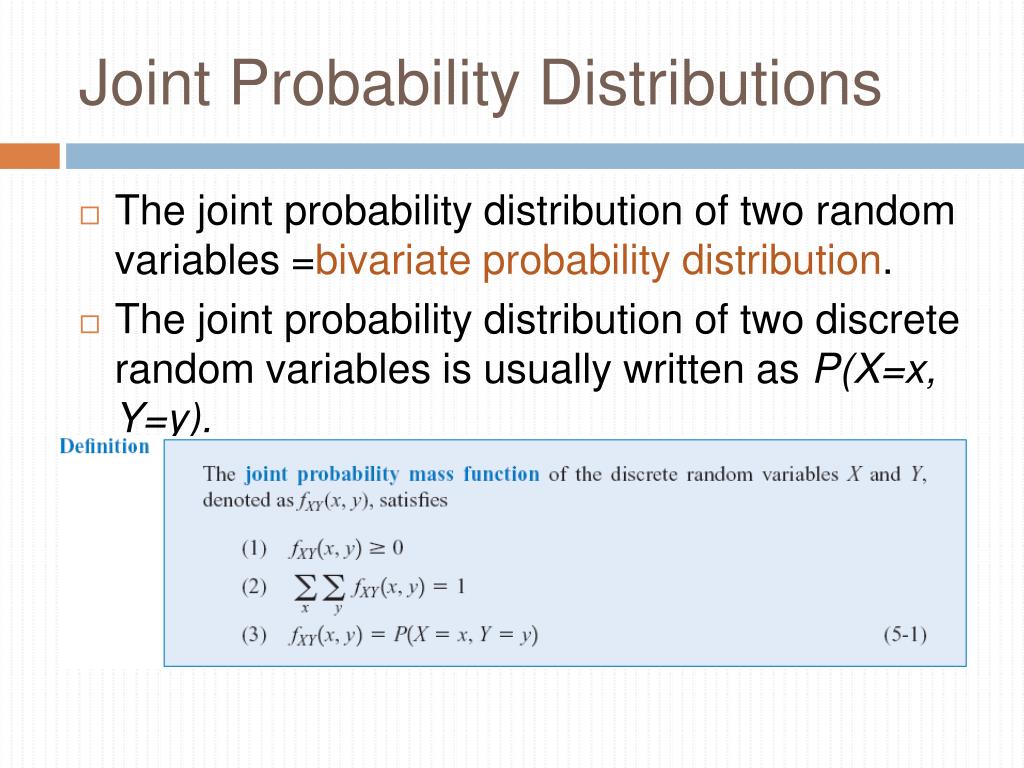


Ppt Joint Probability Distributions Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Http Web Eecs Umich Edu Fessler Course 401 E 94 Fin Pdf


Http Www2 Latech Edu arron Chapter5 Pdf



Home Work Shortcuts 3 13 Two Random Variables X And Y Have The Joint Distribution P 0 0 0 2 P 0 2 0 3 P 1 1 0 1 P 2 0 0 3 P 2 2



The Joint Probability Density Function Of X And Y Is Given By F X Y 67 X2 Xy2 0 Hwmadeeasy
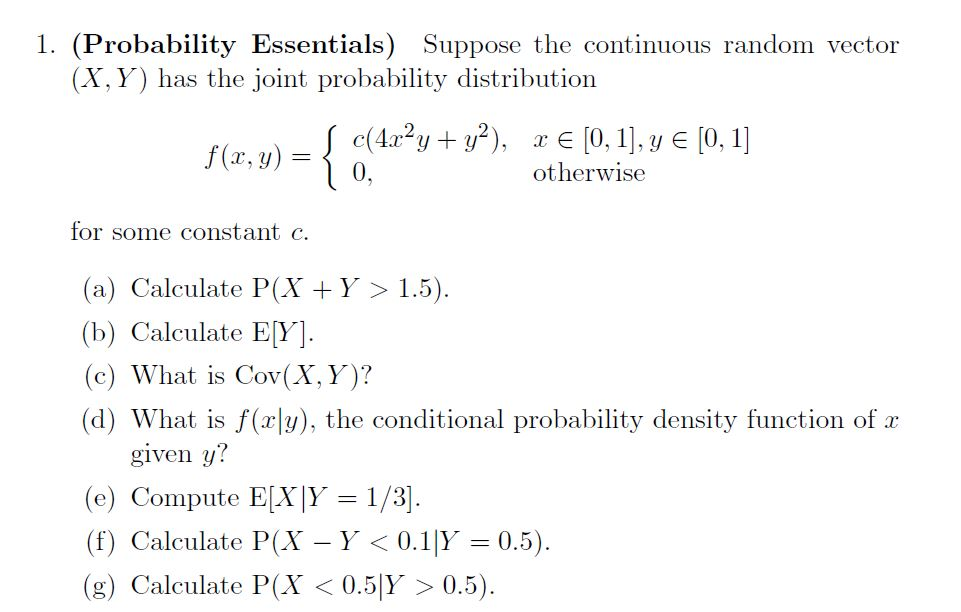


Suppose The Continuous Random Vector X Y Has Th Chegg Com



Variables X And Y Have The Following Joint Probability Mass Function U P X Y 2 2 Homeworklib
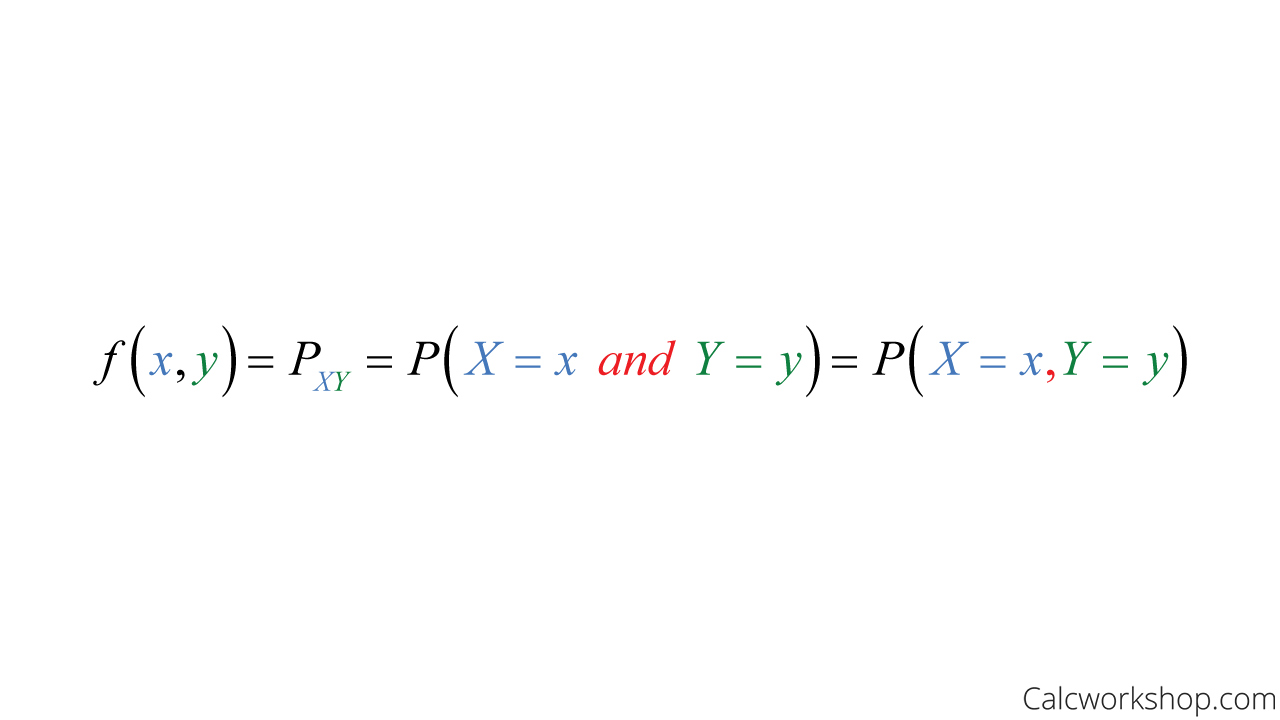


Joint Discrete Random Variables With 5 Examples



Solved 1 Point The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X Chegg Com
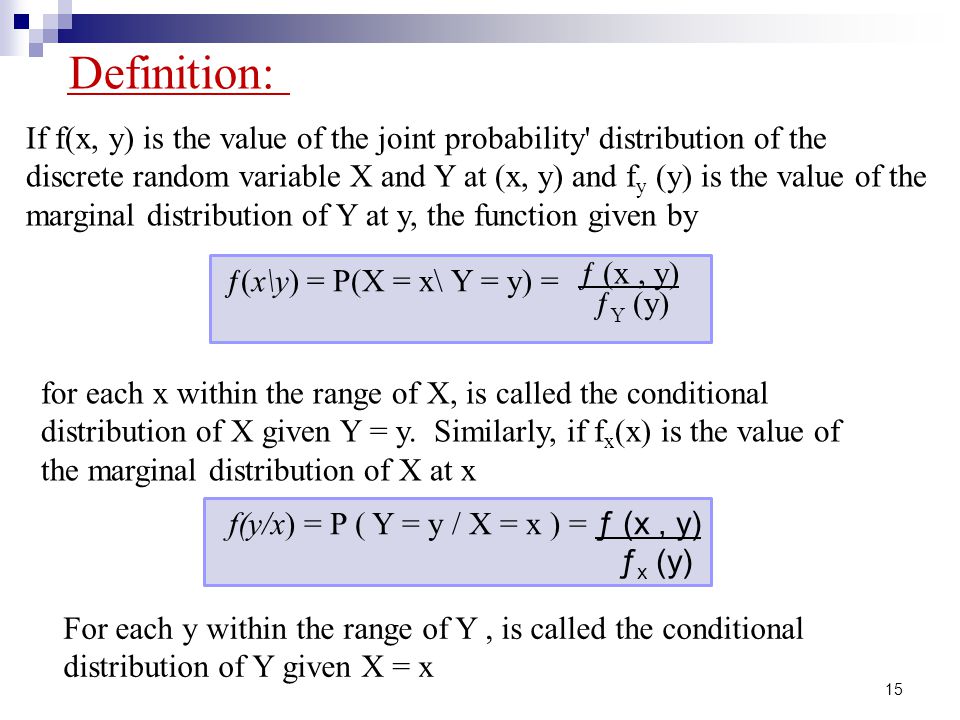


Chapter6 Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download
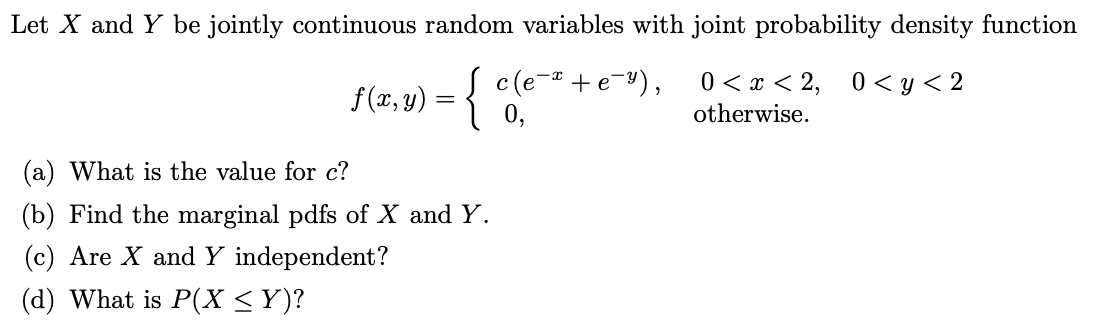


Answered Let X And Y Be Jointly Continuous Bartleby
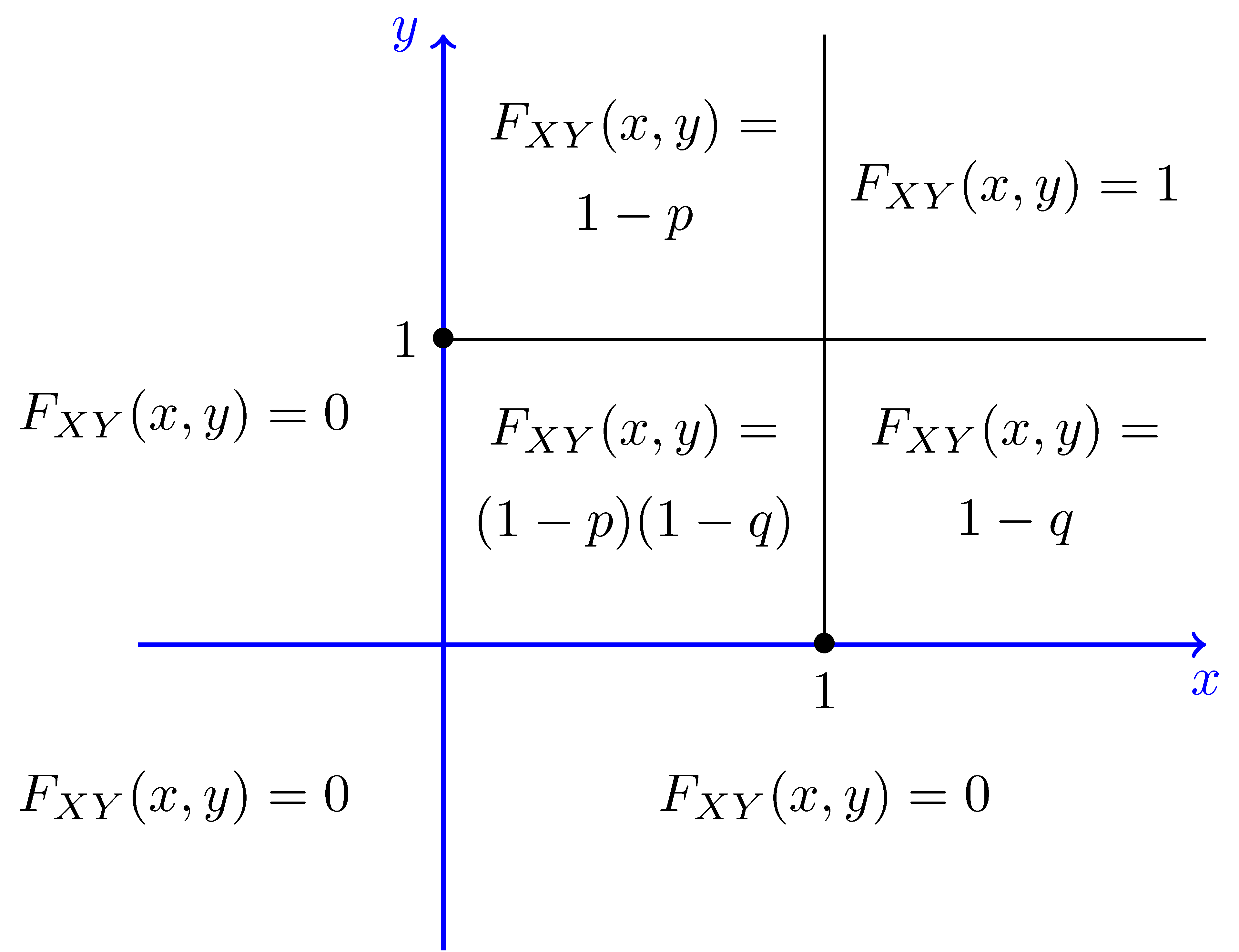


Joint Cumulative Distributive Function Marginal Pmf Cdf



Newbold Chapter 4 Part2 Stat 210 0 Studocu


Www Bauer Uh Edu Rsusmel Phd Sr 6 Pdf


Www Bauer Uh Edu Rsusmel Phd Sr 4 Pdf
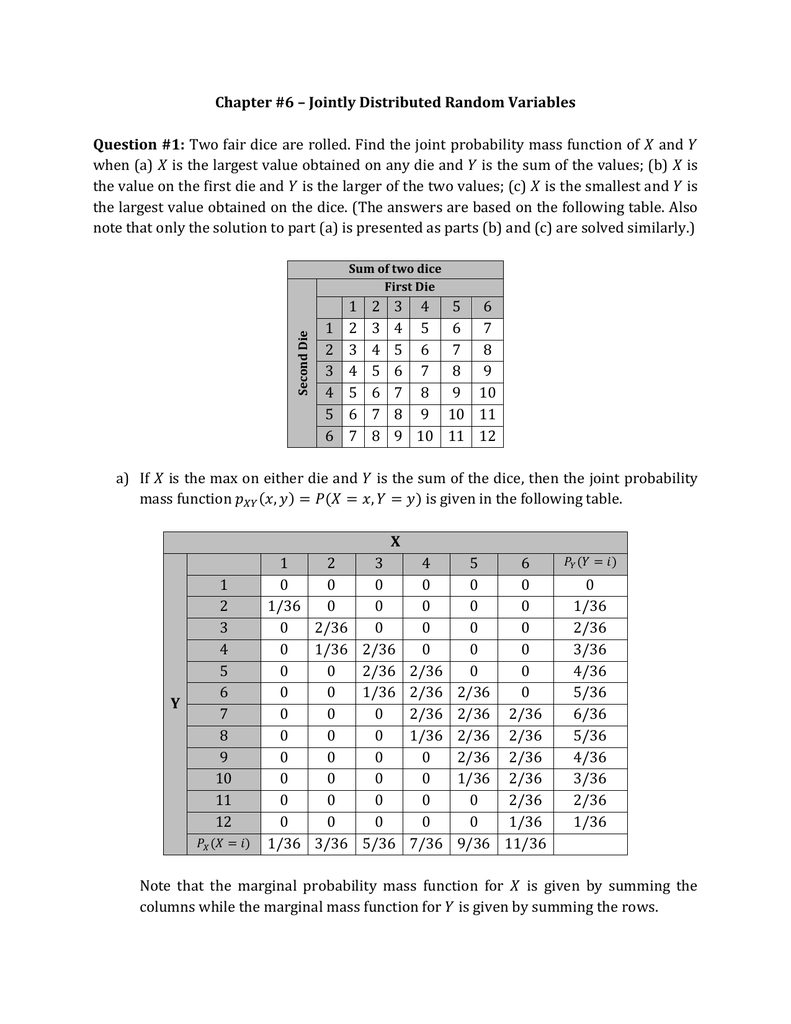


Chapter 6 Jointly Distributed Random Variables Question 1


Joint Probability Formula Examples Investinganswers


Www Utdallas Edu Efrom Solhw Pdf



Solved 1 If The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Chegg Com
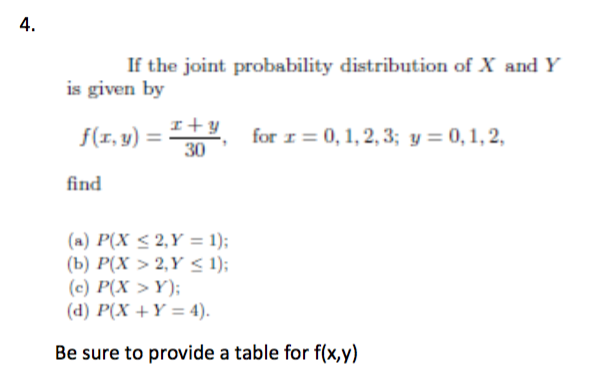


Solved If The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Y I Chegg Com


Q Tbn And9gcr4swpim4yrlzqkoticytkwe S2y8jpun6 Kl0huuhgrbqqco7l Usqp Cau


Journal Of Statistics Education V13n3 Sheldon Stein
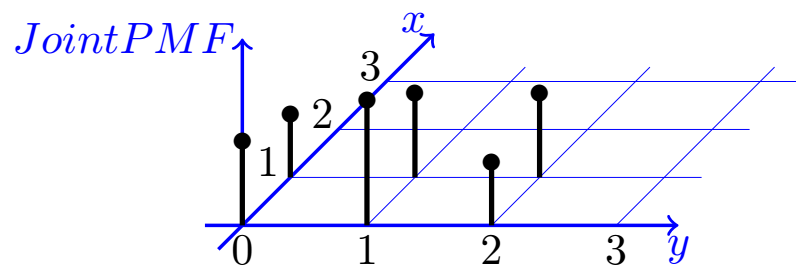


Joint Probability Mass Function Marginal Pmf Pmf



The Joint Probability Density Function Of X And Y Is Given By F X Y E X Y Homeworklib



Mth4106 Introduction To Statistics
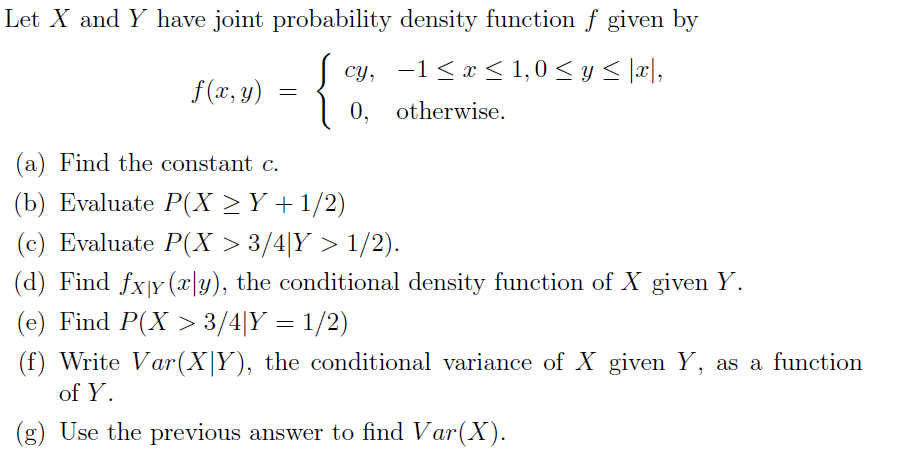


Solved Let X And Y Have Joint Probability Density Functio Chegg Com


コメント
コメントを投稿